How Income Taxes Work
The Internal Revenue Service estimates that taxpayers and businesses spend about 8 billion hours a year complying with tax-filing requirements. To put this into perspective, if all this work were done by a single company, it would need about four million full-time employees and be one of the largest industries in the U.S.1
As complex as the details of taxes can be, the income tax process is fairly straightforward. However, the majority of Americans would rather not spend time with the process, which explains why more than half hire a tax professional to assist in their annual filing.2
Remember, this material is not intended as tax or legal advice. Please consult a professional with tax or legal experience for specific information regarding your individual situation.
Getting Started
The tax process starts with income, and generally, most income received is taxable. A taxpayer’s gross income includes income from work, investments, interest, pensions, as well as other sources. The income from all these sources is added together to arrive at the taxpayers’ total income.
What’s not considered income? Gifts, inheritances, workers’ compensation benefits, welfare benefits, or cash rebates from a dealer or manufacturer.3
From gross income, adjustments are subtracted. These adjustments may include retirement plan contributions, half of self-employment, and other items.
The result is the adjusted gross income (AGI).
From adjusted gross income, deductions are subtracted. With deductions, taxpayers have two choices: the standard deduction or itemized deductions. The following chart provides some details on standard vs. itemized deductions based on 2024 limits:
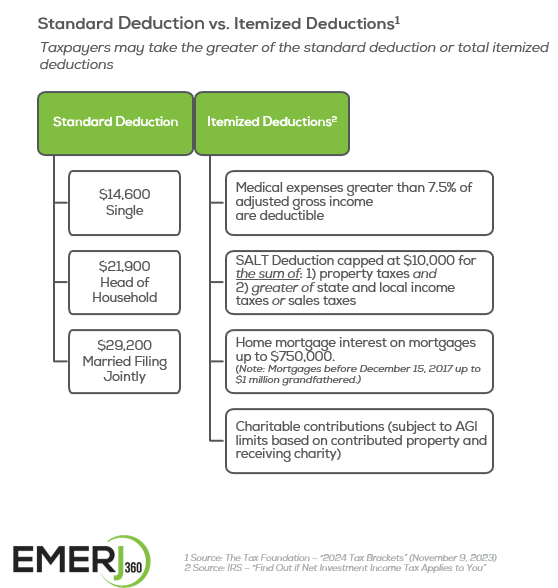
Itemized deductions can include state and local taxes, charitable contributions, the interest on a home mortgage, and certain unreimbursed job expenses, among other things. Keep in mind that there are limits on the amount of state and local taxes that can be deducted.4
Once deductions have been subtracted, the result is taxable income. Taxable income leads to gross tax liability.
Any tax credits are then subtracted from the gross tax liability. Taxpayers may receive credits for a variety of items, including energy-saving improvements.
The result is the taxpayer’s total tax.
Understanding how the tax process works is one thing. Doing the work is quite another. Having this knowledge in the back of your mind can give you a better understanding behind the annual April 15th Tax Day and processes behind it.
Sources:
- NTU.org, April 18, 2022
- IRS.gov, 2023
- The tax code allows an individual to gift up to $17,000 per person in 2023 without triggering any gift or estate taxes. An individual can give away up to $12,920,000 without owing any federal tax. Couples can leave up to $25,840,000 without owing any federal tax. Also, keep in mind that some states may have their own estate tax regulations. This material is not intended as tax or legal advice. Please consult a professional with tax or legal experience for specific information regarding your individual situation.
- The mortgage interest deduction is the first $750,000 of the loan for a home and the state and local income taxes deduction is capped at $10,000.

